Zinc Sulfate(in 1,518 products)
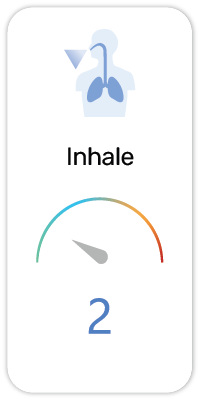
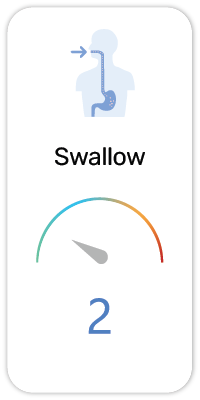
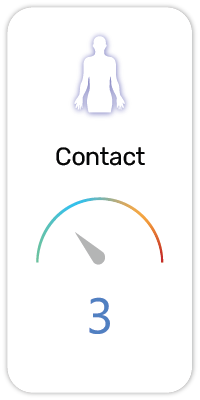
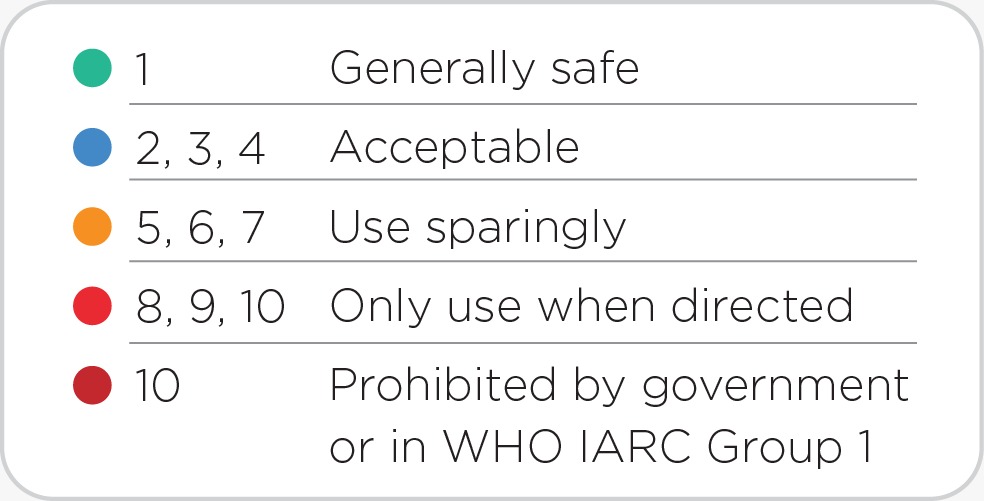
Potential Risk Index®:
About:
Functions:
1. Astringent - Causes the contraction of body tissues, typically of the skin.
2. Dietary / Nutritional Supplement - Vitamins, minerals, proteins, fatty acids or probiotics that improves nutritional intake
Zinc Sulfate is a salt of the essential trace metal zinc. Zinc is involved in tissue repair and is an important constituent of some proteins, including those involved in taste and smell. Zinc sulfate supplementation may prevent radiation-induced ageusia. [1]
Scientific References:
1. PubChem: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/24424
Regulatory References:
1. EU CosIng Annex III, SUBSTANCES WITH RESTRICTIONS IN COSMETIC PRODUCTS [2018]
- Ref: III/24
2. Japan’s List of Designated Food Additives under Article 10 of the Food Sanitation Act
- Zinc salts (limited to Zinc Gluconate and Zinc Sulfate)
3. US FDA Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) (21 CFR 182) [2017]
- § 182.8997 - Zinc sulfate
Safety and Hazards (UN GHS):
1. Harmful if swallowed (H302)
2. Causes serious eye damage (H318)
3. Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child (H361)
4. May cause damage to organs (H371)
5. Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure (H372)
6. Very toxic to aquatic life (H400)
7. Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects (H410)
Potential Health Concerns For:
1. Acidosis (PubMed ID:7265320)
2. Hypotension (PubMed ID:7265320)
3. Hypoxia (PubMed ID:7265320)
4. Necrosis (PubMed ID:19306923)
5. Pneumonia (PubMed ID:19679144)
Potential Health Benefits For:
1. COVID-19 (PubMed ID:32930657)
2. Chemical and Drug Induced Liver Injury (PubMed ID:22422511)
3. Cognition Disorders (PubMed ID:20046642)
4. Fatty Liver, Alcoholic (PubMed ID:20118189)
5. Hepatolenticular Degeneration (PubMed ID:17063115)
6. Hyperglycemia (PubMed ID:12137914)
7. Leishmaniasis, Cutaneous (PubMed ID:15237267)
8. Liver Diseases (PubMed ID:16865776)
9. Migraine Disorders (PubMed ID:21530095)
User Comments:
Submit