Zinc Stearate(in 6,931 products)
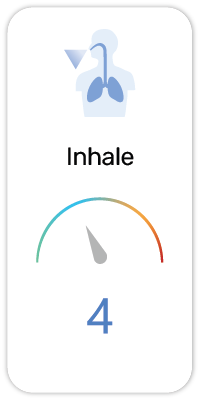
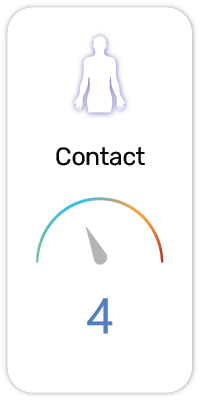
Potential Risk Index®:
About:
Functions:
1. Colorant - Pigments or dyes that are added in order to change or enhance the color.
2. Dietary / Nutritional Supplement - Vitamins, minerals, proteins, fatty acids or probiotics that improves nutritional intake
RELEASING AGENT; LUBRICANT; THICKENING AGENT
Zinc stearate is a "zinc soap" that is widely used industrially. In this context, soap is used in its formal sense, a metal "salt" of a fatty acid. It is a white solid that repels water. It is insoluble in polar solvents such as alcohol and ether but soluble in aromatic hydrocarbons (e.g., benzene) and chlorinated hydrocarbons when heated. It is the most powerful mold release agent among all metal soaps. It contains no electrolyte and has a hydrophobic effect.
It is widely used as a release agent for the production of many kinds of objects: rubber, polyurethane, polyester processing system, powder metallurgy. These applications exploit its "non-stick" properties. In cosmetics, zinc stearate is a lubricant and thickening agent used to improve texture.
Scientific References:
1. PubChem: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/11178
Regulatory References:
1. South Korea - Ministry of Food and Drug Safety - Prohibited/Restricted Chemicals
- Ref: 411
2. EU CosIng Annex IV, COLORANTS ALLOWED IN COSMETIC PRODUCTS [2017]
- Ref: IV/150
3. Association of Southeast Asian Nations Annex IV - Part 1, Allowed Colorants
- Aluminium, zinc, magnesium and calcium stearates
4. US FDA Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) (21 CFR 182) [2017]
- § 182.8994 - Zinc stearate
Safety and Hazards (UN GHS):
1. May cause respiratory irritation (H335)
2. Very toxic to aquatic life (H400)
3. May cause long lasting harmful effects to aquatic life (H413)
User Comments:
Submit