Sodium Fluoride(in 453 products)
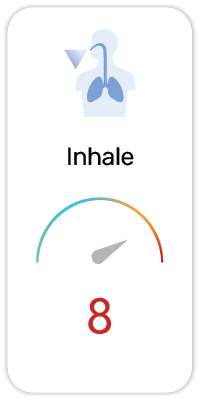
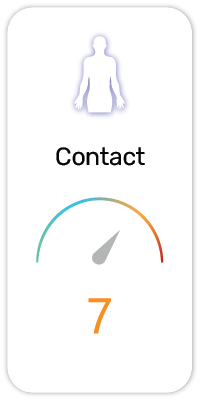
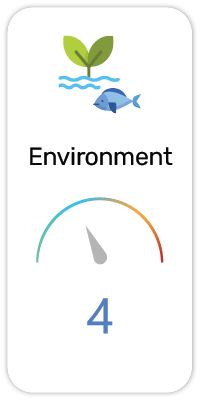
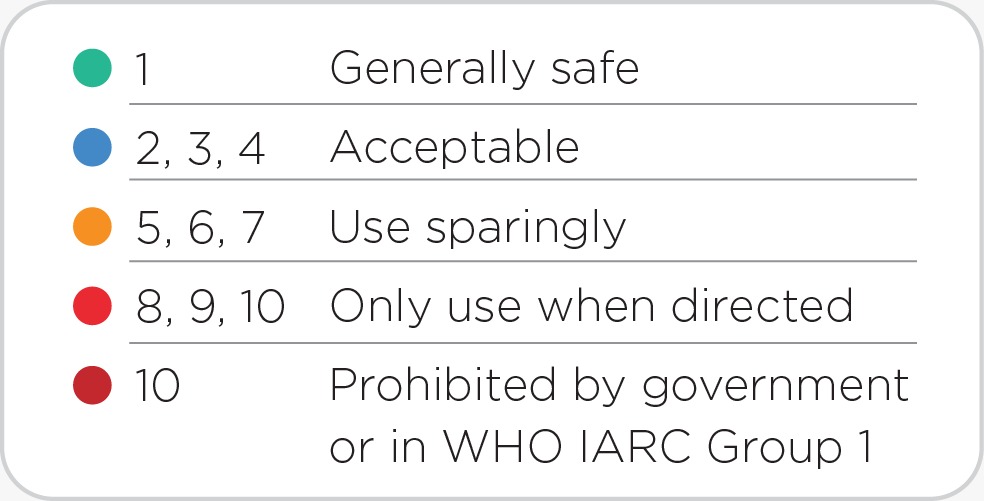
Potential Risk Index®:
About:
Functions:
1. Antiseptic / Disinfectant - Prevents growth of unwanted microorganisms.
2. Drug / Medicine - Treats, alleviates, cures, or prevents sickness. As officially declared by a governmental drug/medicine regulatory body
3. Preservative - Prevents and inhibits the growth of unwanted microorganisms which may be harmful
Sodium fluoride (NaF) is a chemical compound and medication. As a medication, it is primarily used to prevent tooth decay in children older than 6 months in areas where the drinking water is low in fluoride. Sodium fluoride is used as a liquid, pill, or paste by mouth with this use being known as fluoride therapy. [1]
Recent Findings:
Sodium Fluoride is an inorganic salt of fluoride used topically or in municipal water fluoridation systems to prevent dental caries. Fluoride appears to bind to calcium ions in the hydroxyapatite of surface tooth enamel, preventing corrosion of tooth enamel by acids. This agent may also inhibit acid production by commensal oral bacteria. [2] US regulatory authorities recommend a maximum intake of 0.7mg of fluoride per liter of water.
However, this traditional use was based on deception and manipulation due to a conflict of interest. This is explained in a book and documentary called the "Fluoride Deception". [3]
Fluorine is one of the most active elements and causes death in animals near a manufacturing plant producing it, and health problems in workers exposed to it. Continuous or intermittent exposure to inorganic fluorides can lead to appreciable accumulation of fluoride in bone and the development of osteosclerosis and other bone changes (WHO, 1970). [4] ln areas of endemic fluorosis and high poverty, the combination of excessive fluoride intake and nutritional insufficiency may lead not only to crippling skeletal malformations (see, e.g., WHO, 1984) [5] but also to neurological disorders (1955,1963,1970)) [6] and may be associated with hematological abnormalities,1978) [7]. Mottled dental enamel has been found in the teeth of children whose mothers drank water containing 12-18 mg/I. (WHO IARC Monograph Volume 27 (1982)) [8]
EU CosIng Annex III Restriction Information:
Regulation:
(EC) No 344/2013
Annex/Ref#:
III/31
Product Type, body parts:
Oral products
Maximum concentration in ready for use preparation:
0,15 % calculated as F.
When mixed with other fluorine compounds permitted under this Annex, total F concentration must not exceed 0,15 %
Wording of conditions of use and warnings:
Contains sodium fluoride
For any toothpaste with compounds containing fluorine in a concentration of 0.1 to 0.15% calculated as F unless it is already labelled as contra-indicated for children (e.g. "for adult use only") the following labelling is obligatory:
"Children of 6 years and younger: use a pea-sized amount for supervised brushing to minimise swallowing. In case of intake of fluoride from other sources consult a dentist or doctor."
SCCS opinions:
0653/03 - Opinion concerning the Safety of Fluorine Compounds in Oral Hygiene Products for Children under the Age of 6 years
0882/05 - Opinion on the Safety of Fluorine Compounds in Oral Hygiene Products for Children under the Age of 6 Years
1214/09 - Clarification on the Opinions SCCNFP/0653/03 and SCCP/0882/05 on the Safety of Fluorine Compounds in Oral Hygiene Products for Children under the Age of 6 Years
Scientific References:
1. PubChem: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5235
2. Water Fluoridation: A Critical Review of the Physiological Effects of Ingested Fluoride as a Public Health Intervention. (Sci. World J., 2014, 1–10. doi:10.1155/2014/293019)
3. For those who wants to look into the controversy of fluoride, a fairly well done investigatory journalist can be found in the following discussions: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eBZRb-73tLc
5. Fluorine and fluorides. Geneva, World Health Organization, International Programme on Chemical Safety (Environmental Health Criteria 36) [WHO reference, IPCS, 1984]
6. Neurology of endemic skeletal fluorosis (Neurol India. 2009;57:7–12)
7. Fluoride’s Effects on the Formation of Teeth and Bones, and the Influence of Genetics (J Dent Res. 2011 May; 90(5): 552–560 DOI: 10.1177/0022034510384626)
8. Fluoride in precipitation. i. Methodology with fluoride-selective electrode. Atmospheric Environment, 16:99 [WHO reference, 1982]
Regulatory References:
1. CANADA INGREDIENT HOTLIST, List of Ingredients that are Restricted for Use in Cosmetic Products [2019]
- Fluoride containing substances
2. EU CosIng Annex III, SUBSTANCES WITH RESTRICTIONS IN COSMETIC PRODUCTS [2018]
- Ref: III/31
Safety and Hazards (UN GHS):
1. Toxic if swallowed (H301)
2. Causes severe skin burns and eye damage (H314)
3. Causes skin irritation (H315)
4. Causes serious eye damage (H318)
5. Causes serious eye irritation (H319)
6. Suspected of causing genetic defects (H341)
7. Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child (H361)
8. Causes damage to organs (H370)
9. Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure (H372)
10. Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure (H373)
11. Harmful to aquatic life (H402)
12. Harmful to aquatic life with long lasting effects (H412)
Potential Health Concerns For:
1. Alzheimer Disease (PubMed ID:3747724)
2. Body Weight Changes (PubMed ID:30920066)
3. Bone Diseases (PubMed ID:19009284)
4. Brain Edema (PubMed ID:21986897)
5. Chemical and Drug Induced Liver Injury (PubMed ID:21986897)
6. Chromosome Aberrations (PubMed ID:28962382)
7. Cognition Disorders (PubMed ID:19900517)
8. Dental Enamel Hypoplasia (PubMed ID:27257137)
9. Depressive Disorder (PubMed ID:32627286)
10. Drug-Related Side Effects and Adverse Reactions (PubMed ID:982456)
11. Edema (PubMed ID:23707774)
12. Fluorosis, Dental (PubMed ID:27257137)
13. Genital Diseases, Male (PubMed ID:21340527)
14. Hemorrhage (PubMed ID:29758312)
15. Hepatomegaly (PubMed ID:30920066)
16. Hypercholesterolemia (PubMed ID:24384758)
17. Hyperglycemia (PubMed ID:19540901)
18. Hypertrophy (PubMed ID:20859737)
19. Infertility, Female (PubMed ID:24071475)
20. Inflammation (PubMed ID:29758312)
21. Kidney Diseases (PubMed ID:20859737)
22. Learning Disorders (PubMed ID:24759735)
23. Liver Diseases (PubMed ID:20859737)
24. Lung Injury (PubMed ID:29758312)
25. Memory Disorders (PubMed ID:24759735)
26. Micronuclei, Chromosome-Defective (PubMed ID:28089781)
27. Motor Disorders (PubMed ID:31710167)
28. Necrosis (PubMed ID:21986897)
29. Neurobehavioral Manifestations (PubMed ID:32627286)
30. Oligospermia (PubMed ID:23707774)
31. Ovarian Diseases (PubMed ID:29323457)
32. Polyuria (PubMed ID:4688183)
33. Pulmonary Edema (PubMed ID:29758312)
34. Pulmonary Fibrosis (PubMed ID:29758312)
35. Renal Insufficiency (PubMed ID:4688183)
36. Testicular Diseases (PubMed ID:23707774)
37. Tooth Diseases (PubMed ID:28266088)
38. Urination Disorders (PubMed ID:982456)
39. Uterine Diseases (PubMed ID:29323457)
40. Weight Loss (PubMed ID:27237588)
Potential Health Benefits For:
1. Dental Caries (PubMed ID:1771376)
2. Tooth Demineralization (PubMed ID:17153647)
User Comments:
Submit