Protease; Proteinase(in 1,107 products)
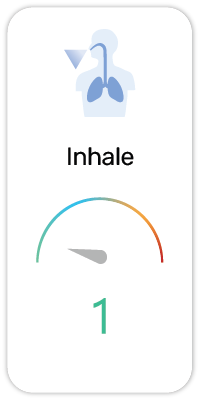
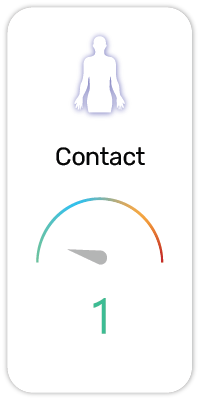
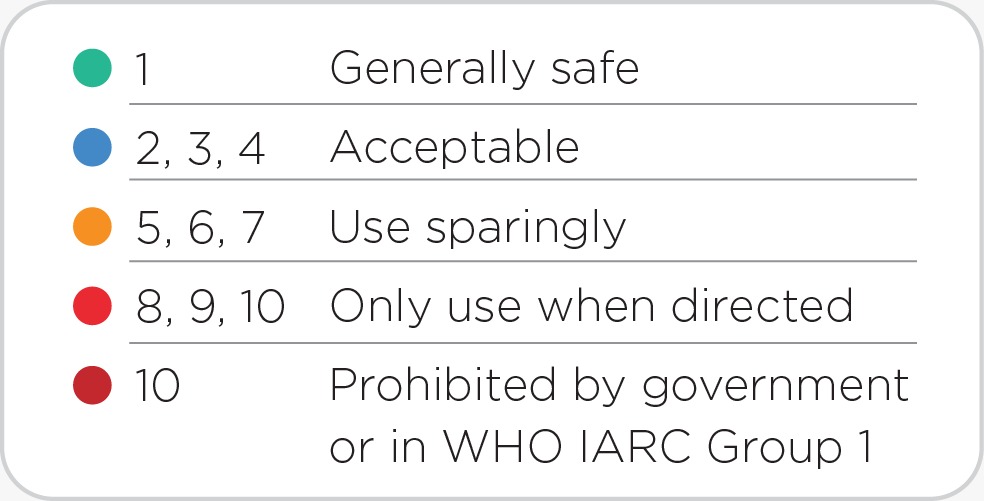
Potential Risk Index®:
About:
Functions:
1. Binder / Stabilizer - Retains the physical characteristics of food/cosmetics and ensure the mixture remains in an even state.
2. Biologics - Biological components such as amino acids and its derivatives which modifies certain functions
3. Dietary / Nutritional Supplement - Vitamins, minerals, proteins, fatty acids or probiotics that improves nutritional intake
4. Emulsifier - Allows water and oils to remain mixed together to form an emulsion.
5. Flavor / Flavoring / Flavor Enhancer - Provides or enhances a particular taste or smell.
A protease, also known as peptidase or proteinase, is a Trypsin that catalyzes proteolysis, the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids. They do this by cleaving the peptide bonds within proteins by hydrolysis, a reaction where water breaks bonds. Proteases are involved in many biological functions, including digestion of ingested proteins, protein catabolism (breakdown of old proteins) and cell signalling.
It has an unapproved E-number (E1101).
Regulatory References:
1. E-numbers which are not found in EU FOOD
- "E1101"
User Comments:
Submit