Dehydroepiandrosterone(in 33 products)
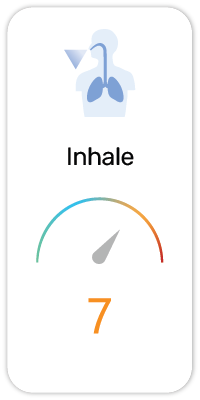
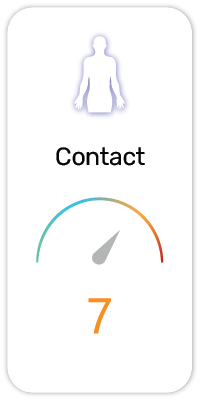
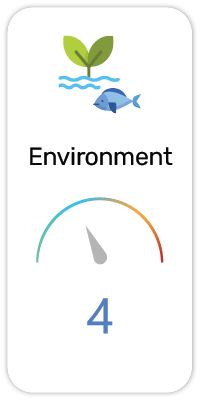
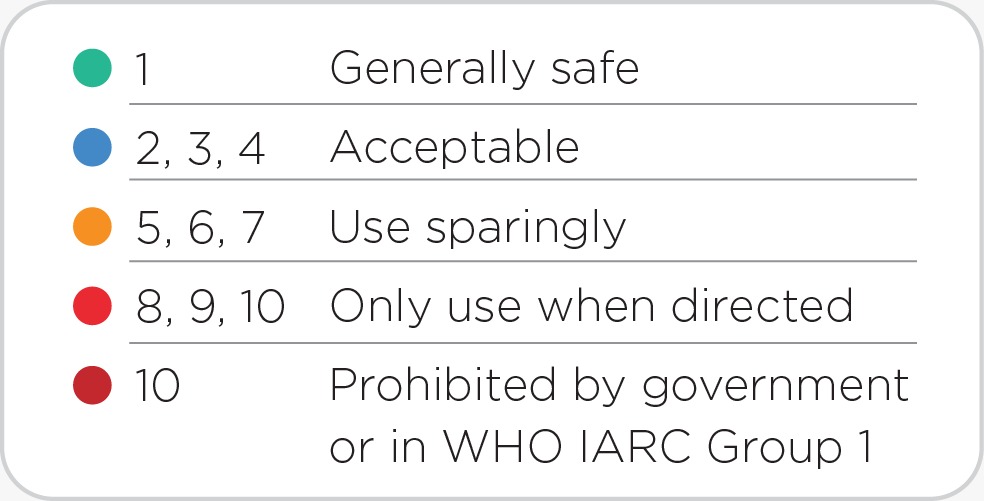
Potential Risk Index®:
About:
Functions:
1. Biologics - Biological components such as amino acids and its derivatives which modifies certain functions
2. Dietary / Nutritional Supplement - Vitamins, minerals, proteins, fatty acids or probiotics that improves nutritional intake
Dehydroepiandrosterone, commonly known as DHEA, is a hormone that occurs naturally in the human body. DHEA is produced by the adrenal glands and plays a crucial role in the synthesis of other hormones, such as estrogen and testosterone.
While DHEA is naturally present in the body, it is also available as a dietary supplement. However, it's important to note that the use of DHEA supplements should be approached with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as hormonal balance is delicate and individual responses may vary.
Historically, DHEA has been the subject of scientific research and has been linked to various potential benefits. Some studies suggest that DHEA may have a role in promoting overall well-being, supporting energy levels, and potentially supporting cognitive function. However, more research is needed to fully understand the extent of these potential benefits.
Fun fact: DHEA levels tend to decline with age, which has led to increased interest in its potential anti-aging properties. However, it's important to approach any claims related to anti-aging effects with a critical mindset and consult with a healthcare professional.
Scientific References:
1. PubChem: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5881
Safety and Hazards (UN GHS):
1. Causes skin irritation (H315)
2. Causes serious eye irritation (H319)
3. May cause respiratory irritation (H335)
4. May damage fertility or the unborn child (H360)
5. May cause harm to breast-fed children (H362)
6. Very toxic to aquatic life (H400)
7. Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects (H410)
Potential Health Concerns For:
1. Adrenal Hyperplasia, Congenital (PubMed ID:3157507)
2. Diabetes Mellitus, Type 1 (PubMed ID:16616286)
3. Disease Models, Animal (PubMed ID:27634381)
4. Insulin Resistance (PubMed ID:27634381)
5. Keratosis (PubMed ID:27634381)
6. Liver Neoplasms (PubMed ID:18709148)
7. Liver Neoplasms, Experimental (PubMed ID:8603461)
8. Panic Disorder (PubMed ID:15996752)
9. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PubMed ID:21062263)
10. Polycythemia (PubMed ID:15161484)
11. Weight Gain (PubMed ID:27634381)
Potential Health Benefits For:
1. Adenocarcinoma (PubMed ID:9131265)
2. Adrenal Insufficiency (PubMed ID:17302879)
3. Catalepsy (PubMed ID:24739405)
4. Cocaine-Related Disorders (PubMed ID:16309898)
5. Feeding and Eating Disorders (PubMed ID:12659879)
6. Hyperglycemia (PubMed ID:11228057)
7. Hypertension (PubMed ID:1387510)
8. Learning Disorders (PubMed ID:15451042)
9. Mammary Neoplasms, Experimental (PubMed ID:16457693)
10. Memory Disorders (PubMed ID:15451042)
11. Osteoporosis, Postmenopausal (PubMed ID:16397352)
12. Prenatal Exposure Delayed Effects (PubMed ID:15451042)
13. Schizophrenia (PubMed ID:24739405)
14. Weight Loss (PubMed ID:12659879)
User Comments:
Submit