Carrageenan(in 10,507 products)
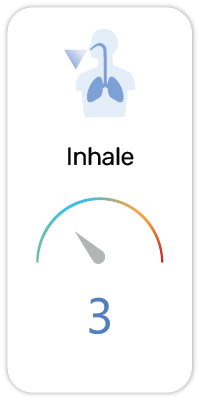
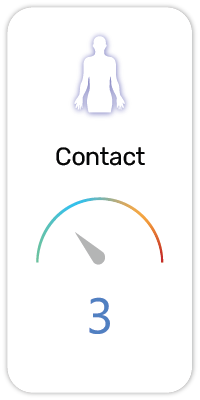
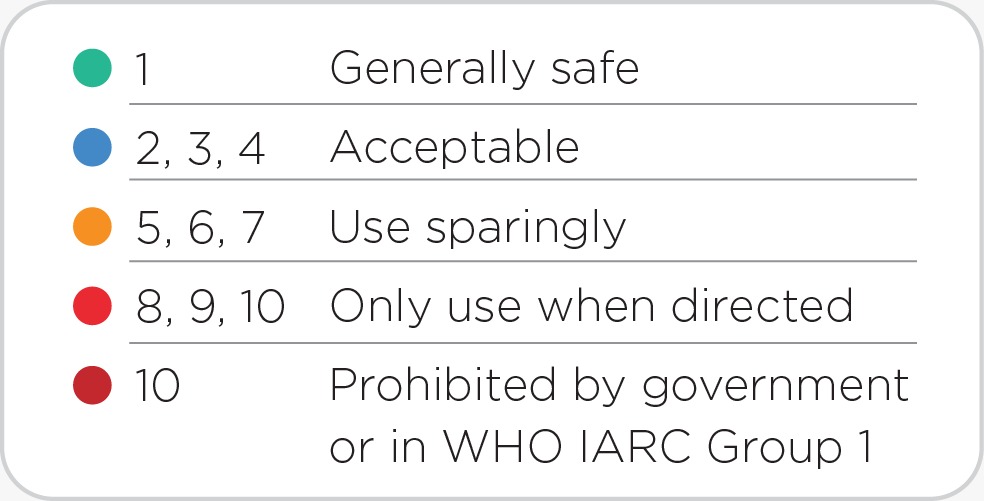
Potential Risk Index®:
About:
Functions:
1. Binder / Stabilizer - Retains the physical characteristics of food/cosmetics and ensure the mixture remains in an even state.
2. Emulsifier - Allows water and oils to remain mixed together to form an emulsion.
3. Gelling Agent / Thickener - Increases the viscosity by thickening the liquid to give it more texture
4. Suspending Agent - Promotes particle suspension or dispersion while reducing sedimentation
Carrageenan or carrageenin is a family of linear sulfated polysaccharides that are extracted from red edible seaweeds. They are widely used in the food industry, for their gelling, thickening, and stabilizing properties (E407). Their main application is in dairy and meat products, due to their strong binding to food proteins. Carrageenans are used in toothpaste as stabilizer to prevent constituents separating. It is also used in shampoo and cosmetic creams as thickener.
Some scientists have presented evidence that carrageenan is highly inflammatory and toxic to the digestive tract, and claim that it may be responsible for colitis, IBS, rheumatoid arthritis, and even colon cancer.
It is approved to use as food additive in EU and generally recognized as safe food substance in US.
Scientific References:
Regulatory References:
1. US FDA Food Additives Status List [2018]
- Carrageenan and its ammonium, calcium, potassium, or sodium salts
2. EU Approved Food Additive [2018]
- E407
3. US FDA Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) (21 CFR 182) [2017]
- § 182.7255 - Chondrus extract
Potential Health Concerns For:
1. Arthritis, Experimental (PubMed ID:15529353)
2. Chromosome Breakage (PubMed ID:9890637)
3. Edema (PubMed ID:10101034)
4. Encephalitis (PubMed ID:22330755)
5. Erythema (PubMed ID:15621379)
6. Granuloma (PubMed ID:18429935)
7. Hyperalgesia (PubMed ID:10193655)
8. Inflammation (PubMed ID:10213916)
9. Lung Injury (PubMed ID:9890637)
10. Nociceptive Pain (PubMed ID:21683763)
11. Pain (PubMed ID:15849840)
12. Peritonitis (PubMed ID:23872256)
13. Pleural Effusion (PubMed ID:9890637)
14. Pleurisy (PubMed ID:11181422)
15. Prostatic Diseases (PubMed ID:28844677)
16. Striatonigral Degeneration (PubMed ID:22330755)
17. Synovitis (PubMed ID:6830329)
18. Weight Loss (PubMed ID:28844677)
Potential Health Benefits For:
1. Fibrosarcoma (PubMed ID:10962813)
2. Papillomavirus Infections (PubMed ID:21483020)
User Comments:
Submit