Pantothenic Acid(in 2,440 products)
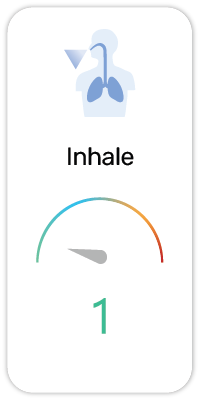
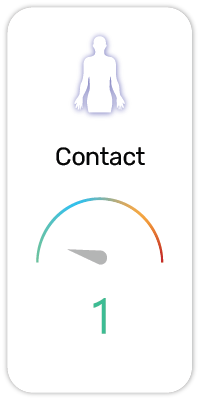
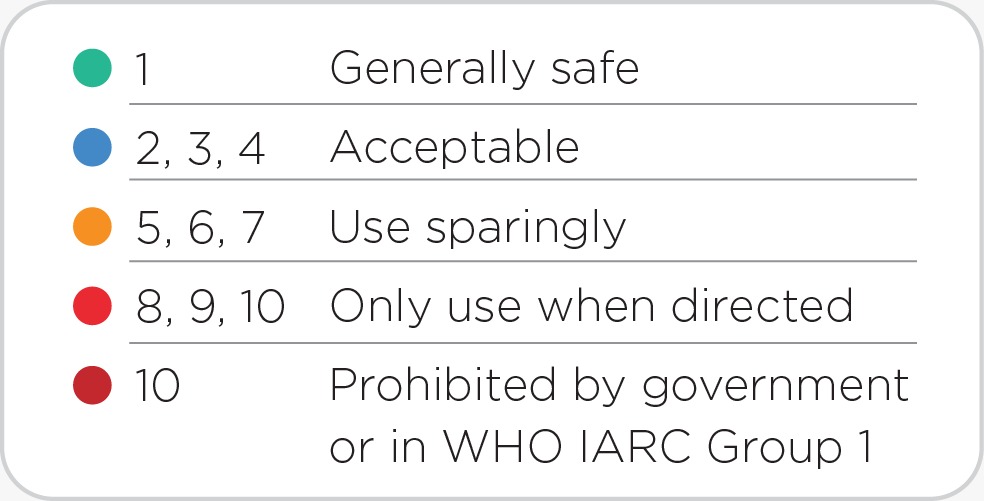
Potential Risk Index®:
About:
Functions:
1. Antistatic Agent - Reduces or eliminates the build up of static electricity.
2. Dietary / Nutritional Supplement - Vitamins, minerals, proteins, fatty acids or probiotics that improves nutritional intake
Skin Conditioning Agents Skin Conditioning Agents
Pantothenic acid is used in the synthesis of coenzyme A ( CoA ). Coenzyme A may act as an acyl group carrier to form acetyl-CoA and other related compounds; this is a way to transport carbon atoms within the cell. CoA is important in energy metabolism for pyruvate to enter the tricarboxylic acid cycle ( TCA cycle) as acetyl-CoA , and for ?- ketoglutarate to be transformed to succinyl-CoA in the cycle. CoA is also important in the biosynthesis of many important compounds such as fatty acids, cholesterol , and acetylcholine . CoA is incidentally also required in the formation of ACP, which is also required for fatty acid synthesis in addition to CoA . Pantothenic acid in the form of CoA is also required for acylation and acetylation, which, for example, are involved in signal transduction and enzyme activation and deactivation, respectively. Since pantothenic acid participates in a wide array of key biological roles, it is essential to all forms of life. As such, deficiencies in pantothenic acid may have numerous wide-ranging effects, as discussed below. Pantothenic Acid is a water -soluble vitamin ubiquitously found in plants and animal tissues with antioxidant property. Vitamin B5 is a component of coenzyme A ( CoA ) and a part of the vitamin B2 complex. Vitamin B5 is a growth factor and is essential for various metabolic functions, including the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fatty acids. This vitamin is also involved in the synthesis of cholesterol , lipids, neurotransmitters, steroid hormones, and hemoglobin.
Scientific References:
1. PubChem: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/6613
Regulatory References:
1. US FDA Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) Food Substances (21 CFR 184) [2017]
- § 184.1945 - Vitamin B
Potential Health Concerns For:
1. Arthritis, Experimental (PubMed ID:24709313)
2. Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2 (PubMed ID:27094034)
Potential Health Benefits For:
1. Abnormalities, Drug-Induced (PubMed ID:16112698)
2. Drug-Related Side Effects and Adverse Reactions (PubMed ID:17379144)
3. Neoplasms (PubMed ID:6061664)
4. Neural Tube Defects (PubMed ID:16112698)
5. Prenatal Injuries (PubMed ID:16112698)
6. Wounds, Nonpenetrating (PubMed ID:19397697)
User Comments:
Submit