Cholecalciferol(in 3,231 products)
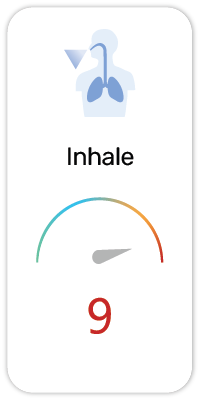
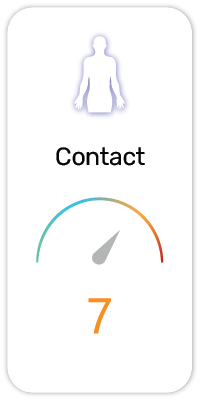
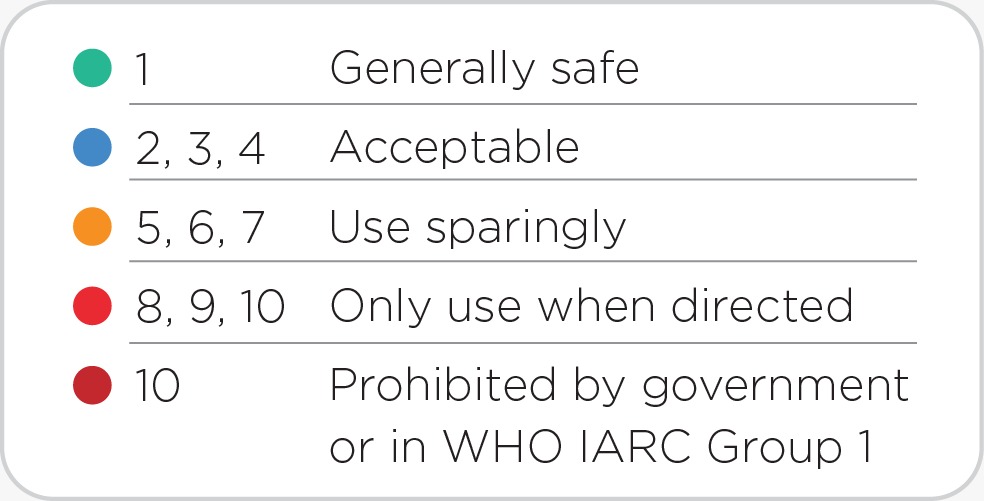
Potential Risk Index®:
About:
Functions:
1. Dietary / Nutritional Supplement - Vitamins, minerals, proteins, fatty acids or probiotics that improves nutritional intake
2. Drug / Medicine - Treats, alleviates, cures, or prevents sickness. As officially declared by a governmental drug/medicine regulatory body
3. Insecticide / Pesticide - Kills or inhibits unwanted organisms
Cholecalciferol ( vitamin D3 ) is a steroid hormone that has long been known for its important role in regulating body levels of calcium and phosphorus, in mineralization of bone, and for the assimilation of Vitamin A. The classical manifestations of vitamin D deficiency is rickets, which is seen in children and results in bony deformities including bowed long bones. Deficiency in adults leads to disease osteomalacia. Both rickets and osteomalacia reflect impaired mineralization of newly synthesized bone matrix, and usually result from a combination of inadequate exposure to sunlight and decreased dietary intake of vitamin D. Common causes of vitamin D deficiency include genetic defects in the vitamin D receptor, severe liver or kidney disease, and insufficient exposure to sunlight. Vitamin D plays an important role in maintaining calcium balance and in the regulation of parathyroid hormone (PTH). It promotes renal reabsorption of calcium, increases intestinal absorption of calcium and phosphorus, and increases calcium and phosphorus mobilization from bone to plasma. Cholecalciferol is a steroid hormone produced in the skin when exposed to ultraviolet light or obtained from dietary sources. The active form of cholecalciferol, 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol (calcitriol) plays an important role in maintaining blood calcium and phosphorus levels and mineralization of bone. The activated form of cholecalciferol binds to vitamin D receptors and modulates gene expression. This leads to an increase in serum calcium concentrations by increasing intestinal absorption of phosphorus and calcium, promoting distal renal tubular reabsorption of calcium and increasing osteoclastic resorption. [1]
Scientific References:
Regulatory References:
1. Association of Southeast Asian Nations Annex II, Prohibited
- Ergocalciferol (INN) and Cholecalciferol (vitamins D2 and D3)
2. South Korea - Ministry of Food and Drug Safety - Prohibited/Restricted Chemicals
- Ref: 745
3. CANADA INGREDIENT HOTLIST, List of Ingredients that are Restricted for Use in Cosmetic Products [2019]
- Vitamin D3
4. Japan’s List of Designated Food Additives under Article 10 of the Food Sanitation Act
- Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3)
5. WHO Model List of Essential Medicines [2019]
- colecalciferol
6. US FDA Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) Food Substances (21 CFR 184) [2017]
- § 184.1950 - Vitamin D
Safety and Hazards (UN GHS):
1. Fatal if swallowed (H300)
2. Toxic if swallowed (H301)
3. Fatal in contact with skin (H310)
4. Toxic in contact with skin (H311)
5. Fatal if inhaled (H330)
6. May damage fertility or the unborn child (H360)
7. Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure (H372)
Potential Health Concerns For:
1. Acute Kidney Injury (PubMed ID:19856155)
2. Adrenal Gland Diseases (PubMed ID:10496673)
3. Aortic Diseases (PubMed ID:12803500)
4. Arteriosclerosis (PubMed ID:1648535)
5. Atherosclerosis (PubMed ID:19931584)
6. Calcinosis (PubMed ID:12803500)
7. Cardiomegaly (PubMed ID:2154115)
8. Child Nutrition Disorders (PubMed ID:21048240)
9. Coronary Artery Disease (PubMed ID:1648535)
10. Drug Hypersensitivity (PubMed ID:2995910)
11. Drug-Related Side Effects and Adverse Reactions (PubMed ID:3380067)
12. Gastrointestinal Diseases (PubMed ID:15460982)
13. Growth Disorders (PubMed ID:14968361)
14. Hypercalcemia (PubMed ID:10490077)
15. Hypercalciuria (PubMed ID:19185560)
16. Hyperphosphatemia (PubMed ID:10490077)
17. Hyperplasia (PubMed ID:10496673)
18. Hypertension (PubMed ID:15460982)
19. Lithiasis (PubMed ID:21670126)
20. Muscle Hypotonia (PubMed ID:14968361)
21. Pheochromocytoma (PubMed ID:10496673)
22. Polymyositis (PubMed ID:20427501)
23. Renal Insufficiency (PubMed ID:15460982)
24. Vascular Calcification (PubMed ID:23104429)
25. Vascular Diseases (PubMed ID:16378124)
26. Vitamin D Deficiency (PubMed ID:2154115)
27. Weight Loss (PubMed ID:10490077)
Potential Health Benefits For:
1. Autoimmune Diseases (PubMed ID:16142846)
2. Colitis (PubMed ID:33974900)
3. Fatty Liver (PubMed ID:29653100)
4. Hypocalcemia (PubMed ID:80633)
5. Inflammation (PubMed ID:25673501)
6. Liver Cirrhosis (PubMed ID:29653100)
7. Mammary Neoplasms, Experimental (PubMed ID:21843606)
8. Mental Disorders (PubMed ID:27597724)
9. Muscle Cramp (PubMed ID:1657745)
10. Musculoskeletal Pain (PubMed ID:23149532)
11. Neoplasms, Experimental (PubMed ID:32640329)
12. Neural Tube Defects (PubMed ID:25673501)
13. Osteomalacia (PubMed ID:1013714)
14. Osteoporosis, Postmenopausal (PubMed ID:25299349)
15. Pain (PubMed ID:25299349)
16. Placenta Diseases (PubMed ID:25673501)
17. Precancerous Conditions (PubMed ID:28634113)
18. Prostatic Neoplasms (PubMed ID:17024972)
19. Rickets (PubMed ID:21048240)
20. Sunburn (PubMed ID:28576736)
21. Testicular Diseases (PubMed ID:34051273)
22. Thyrotoxicosis (PubMed ID:1657745)
User Comments:
Submit