Sodium Bicarbonate(in 7,266 products)
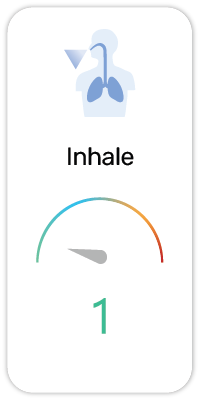
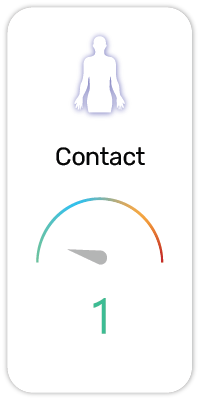
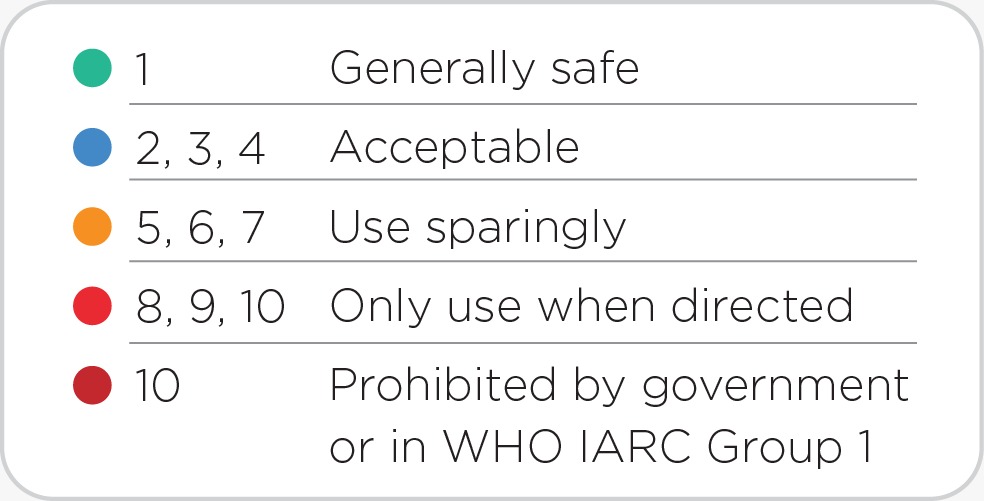
Potential Risk Index®:
About:
Functions:
1. Acidity Regulator / Buffering Agent - Changes or maintains the acidity or basicity of food/cosmetics.
2. Fragrance / Fragrance Component - Provides or enhances a particular smell or odor.
3. Leavening / Raising Agent - Causes or forms gas bubbles in food
Sodium bicarbonate (IUPAC: sodium hydrogen carbonate), commonly known as baking soda. Sodium bicarbonate is a white solid that is crystalline but often appears as a fine powder. It has a slightly salty, alkaline taste resembling that of washing soda (sodium carbonate). [1]
Sodium bicarbonate has a wide variety of uses. In cooking, sodium bicarbonate referred to as baking soda, is primarily used in baking as a leavening agent. It reacts with acidic components in batters, releasing carbon dioxide, which causes expansion of the batter and forms the characteristic texture and grain in pancakes, cakes, quick breads, soda bread, and other baked and fried foods. Baking soda may be used together with sourdough, which is acidic, making a lighter product with a less acid taste. [1]
In personal hygiene, toothpaste containing sodium bicarbonate can enhance whitening and plaque removal effect. It is also used as an ingredient in some mouthwashes. It has anticaries and abrasive properties. It works as a mechanical cleanser on the teeth and gums, neutralizes the production of acid in the mouth, and also acts as an antiseptic to help prevent infections. in combination with other ingredients, it can be used to make a dry or wet deodorant. [1]
Scientific References:
1. PubChem: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/516892
Regulatory References:
1. Japan’s List of Designated Food Additives under Article 10 of the Food Sanitation Act
- Sodium Bicarbonate (Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate or Bicarbonate Soda)
2. Canada List of Permitted Food Additives
- List 8 - Sodium Bicarbonate
3. US FDA Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) Food Substances (21 CFR 184) [2017]
- § 184.1736 - Sodium bicarbonate
Safety and Hazards (UN GHS):
1. Causes serious eye irritation (H319)
Potential Health Concerns For:
1. Acute Kidney Injury (PubMed ID:25559736)
2. Albuminuria (PubMed ID:10430982)
3. Alkalosis (PubMed ID:6858403)
4. Calcinosis (PubMed ID:6309480)
5. Dermatitis, Irritant (PubMed ID:22906572)
6. Hypercalcemia (PubMed ID:625456)
7. Hypotension (PubMed ID:236705)
8. Infant, Newborn, Diseases (PubMed ID:6309480)
9. Myoclonus (PubMed ID:8835608)
10. Nephrolithiasis (PubMed ID:625456)
11. Papilloma (PubMed ID:1752781)
12. Precancerous Conditions (PubMed ID:1752781)
13. Sinus Arrest, Cardiac (PubMed ID:15767228)
14. Urinary Bladder Neoplasms (PubMed ID:1752781)
15. Vascular Diseases (PubMed ID:6309480)
Potential Health Benefits For:
1. Acid-Base Imbalance (PubMed ID:10452435)
2. Acidosis (PubMed ID:11490519)
3. Arrhythmias, Cardiac (PubMed ID:10452435)
4. Bradycardia (PubMed ID:15767228)
5. Confusion (PubMed ID:20736205)
6. Consciousness Disorders (PubMed ID:20548984)
7. Drug-Related Side Effects and Adverse Reactions (PubMed ID:10078349)
8. Dyspareunia (PubMed ID:8386779)
9. Dyspnea (PubMed ID:20016425)
10. Fanconi Syndrome (PubMed ID:15230715)
11. Gas Poisoning (PubMed ID:20016425)
12. Heart Diseases (PubMed ID:7661425)
13. Hyperkalemia (PubMed ID:11499566)
14. Kidney Diseases (PubMed ID:10430982)
15. Kidney Failure, Chronic (PubMed ID:9574465)
16. Meniere Disease (PubMed ID:11700197)
17. Nephrocalcinosis (PubMed ID:11490519)
18. Nervous System Diseases (PubMed ID:8987970)
19. Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (PubMed ID:16669738)
20. Organophosphate Poisoning (PubMed ID:6298988)
21. Pain (PubMed ID:12879672)
22. Renal Insufficiency (PubMed ID:15150204)
23. Seizures (PubMed ID:11824763)
24. Sjogren's Syndrome (PubMed ID:11490519)
25. Tachycardia, Ventricular (PubMed ID:10465245)
26. Torsades de Pointes (PubMed ID:15837031)
27. Urinary Bladder Calculi (PubMed ID:3712608)
28. Ventricular Dysfunction (PubMed ID:3017159)
29. Ventricular Dysfunction, Left (PubMed ID:11308123)
User Comments:
Submit