Papain(in 1,369 products)
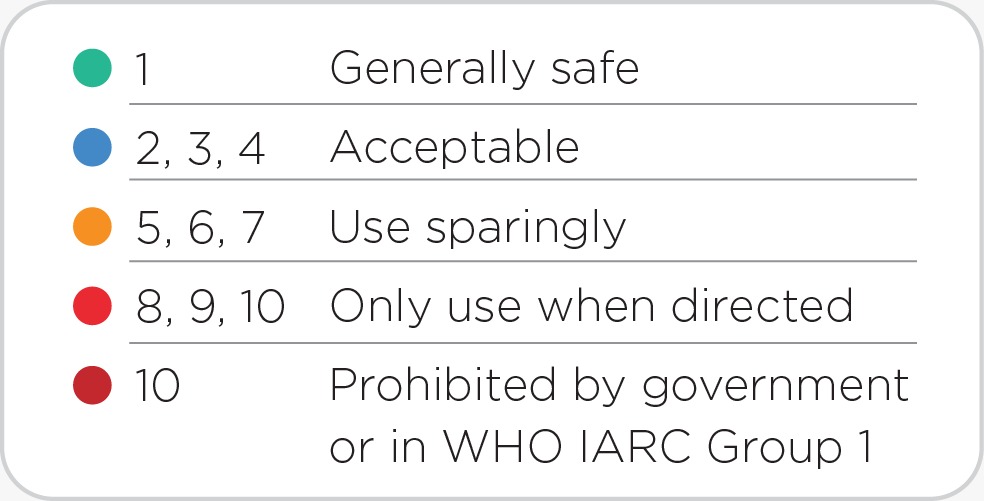
Potential Risk Index®:
About:
Functions:
1. Antistatic Agent - Reduces or eliminates the build up of static electricity.
2. Binder / Stabilizer - Retains the physical characteristics of food/cosmetics and ensure the mixture remains in an even state.
3. Biologics - Biological components such as amino acids and its derivatives which modifies certain functions
4. Flavor / Flavoring / Flavor Enhancer - Provides or enhances a particular taste or smell.
Papain is taken from the fruit of the papaya tree. It is also known as papaya proteinase I, is a cysteine protease enzyme present in papaya and mountain papaya. [1]
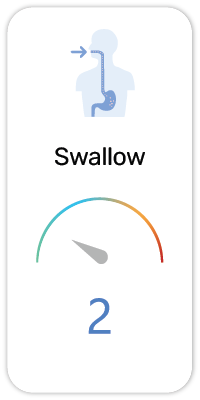
Papain is used to make medicine for pain and swelling relief. Papain can apply directly to the skin to treat insect or animal bites, infected wounds, sores, and ulcers. In manufacturing, papain is used in cosmetics, toothpaste, contact lens cleaners, meat tenderizers, and meat products. [2]
It has an unapproved E-number (E1101i).
Scientific References:
1. PubChem: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/9369
Regulatory References:
1. US FDA Food Additives Status List [2018]
- Papain
2. E-numbers which are not found in EU FOOD
- "E1101ii"
3. US FDA Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) Food Substances (21 CFR 184) [2017]
- § 184.1585 - Papain
Safety and Hazards (UN GHS):
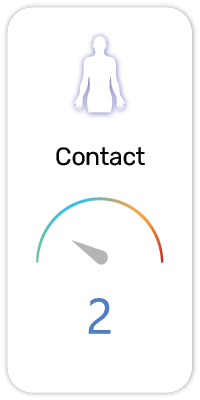
1. Causes skin irritation (H315)
2. Causes serious eye irritation (H319)
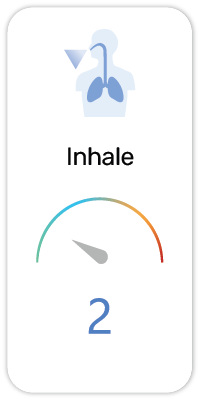
3. May cause allergy or asthma symptoms or breathing difficulties if inhaled (H334)
4. May cause respiratory irritation (H335)
User Comments:
Submit