Ginkgo Biloba Extract(in 628 products)
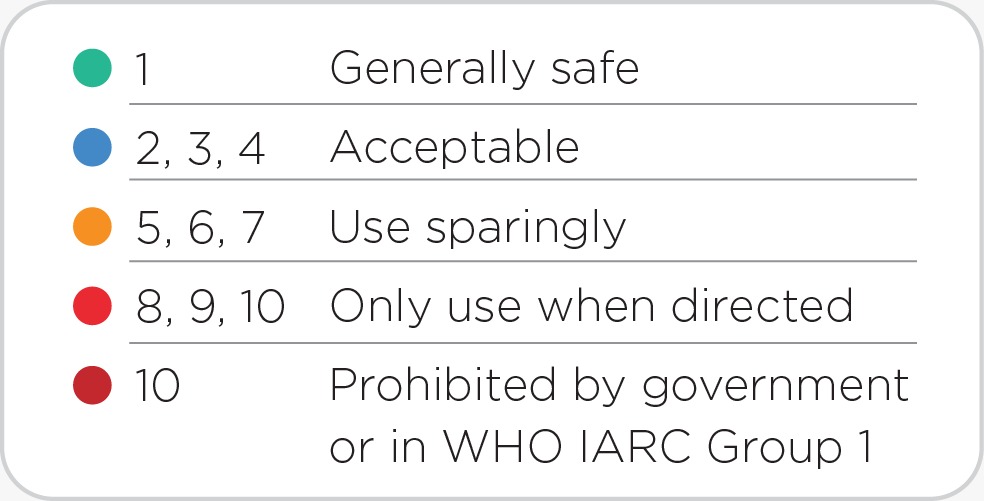
Potential Risk Index®:
About:
Chloroquine is the prototype anti malarial drug, most widely used to treat all types of malaria except for disease caused by chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum. It is highly effective against erythrocytic forms of Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium ovale and Plasmodium malariae, sensitive strains of Plasmodium falciparum, and gametocytes of Plasmodium vivax. Being alkaline, the drug reaches a high concentration within the food vacuoles of the parasite and raises its pH. It is found to induce rapid clumping of the pigment. Chloroquine inhibits the parasitic enzyme heme polymerase that converts the toxic heme into non-toxic hemozoin, thereby resulting in the accumulation of toxic heme within the parasite. It may also interfere with the biosynthesis of nucleic acids. [1]
Chloroquine Phosphate is the phosphate salt of chloroquine, a quinoline compound with antimalarial and anti-inflammatory properties. Chloroquine is the most widely used drug against malaria, except for those cases caused by chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium falciparum. Although the mechanism of action is not fully understood, chloroquine is shown to inhibit the parasitic enzyme heme polymerase that converts the toxic heme into non-toxic hemazoin, thereby resulting in the accumulation of toxic heme within the parasite. Chloroquine may also interfere with the biosynthesis of nucleic acids. [1]
Chloroquine is a 4-aminoquinoline with antimalarial, anti-inflammatory, and potential chemosensitization and radiosensitization activities. Although the mechanism is not well understood, chloroquine is shown to inhibit the parasitic enzyme heme polymerase that converts the toxic heme into non-toxic hemozoin, thereby resulting in the accumulation of toxic heme within the parasite. This agent may also interfere with the biosynthesis of nucleic acids. Chloroquine's potential chemosensitizing and radiosensitizing activities in cancer may be related to its inhibition of autophagy, a cellular mechanism involving lysosomal degradation that minimizes the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) related to tumor reoxygenation and tumor exposure to chemotherapeutic agents and radiation. [1]
Recent Findings:
Ginkgo biloba extract is one of four herbal preparations refunded by health insurance in Germany, on prescription by a medical doctor (AMR, 2013).
In the Ginkgo Evaluation of Memory (GEM) study, ginkgo was used for the prevention of dementia. All 3069 participants were aged 75 years and older. "Of the 310 hospitalizations for cancer, 162 occurred in the group receiving gingko, and 148 occurred in the group receiving placebo". Despite the ginkgo group having 10% more cancer incidents in comparison to the placebo, which is statistically significant, if other factors such as age were also factored in, statistical significance is reduced. As it was also a long term trial over a period of 6 years, the study admitted that "incident cancers not resulting in hospitalization may have been missed and the follow-up was short, so the statistical power for cancer was low, and long-term carcinogenic effects due to exposure could not be evaluated".
In animal studies conducted on mice, in 0, 200, 600, 2000mg/kg of ginkgo biloba extract doses, the study found that "In males, the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma, hepatocellular adenoma or carcinoma (combined), and hepatoblastoma was significantly increased in the groups receiving the lowest, intermediate, and highest dose, and had a significant positive trend."
The experiments described in the IARC report could be construed to be inconclusive.
Scientific References:
1. PubChem: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/2719
Regulatory References:
1. WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) - Group 2B [2018]
- Ginkgo biloba extract
Safety and Hazards (UN GHS):
1. Harmful if swallowed (H302)
Potential Health Concerns For:
1. Catalepsy (PubMed ID:16258634)
2. Coma (PubMed ID:10836866)
3. Fatty Liver (PubMed ID:28564578)
4. Kidney Diseases (PubMed ID:28564578)
5. Paralysis (PubMed ID:18762355)
Potential Health Benefits For:
1. Alzheimer Disease (PubMed ID:12396081)
2. Arrhythmias, Cardiac (PubMed ID:11485048)
3. Bone Diseases, Metabolic (PubMed ID:19356626)
4. Cardiomyopathies (PubMed ID:11485048)
5. Cognition Disorders (PubMed ID:12396081)
6. Learning Disorders (PubMed ID:10672254)
7. Memory Disorders (PubMed ID:10672254)
8. Nerve Degeneration (PubMed ID:12396081)
9. Neurotoxicity Syndromes (PubMed ID:21827809)
User Comments:
Submit