Caffeic Acid(in 32 products)
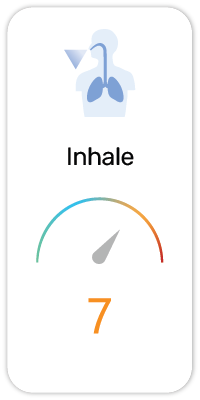
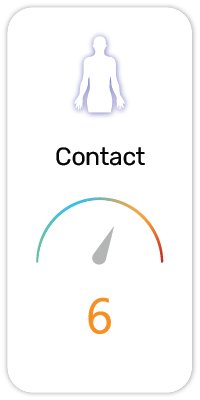
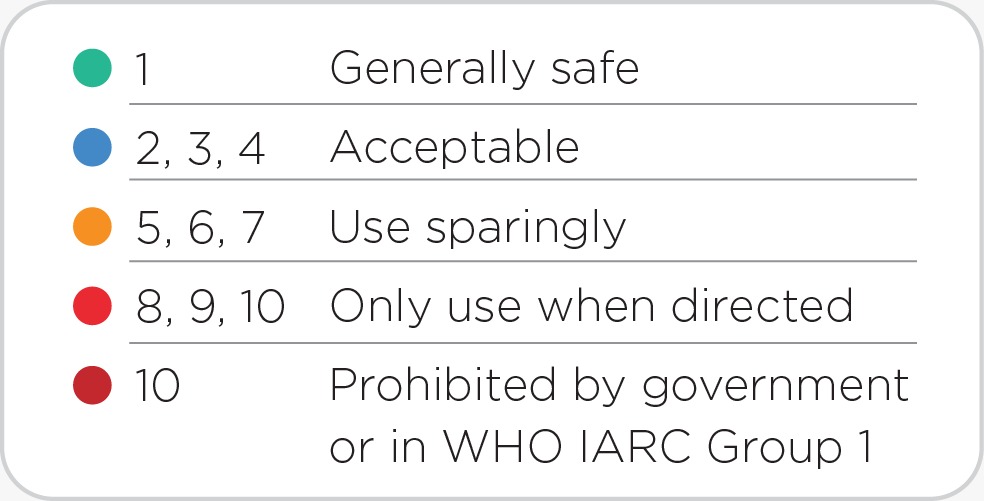
Potential Risk Index®:
About:
Functions:
1. Antioxidant - Reduces oxidation to prevent the formation of free radicals which may be harmful to health.
Caffeic Acid is an orally bioavailable, hydroxycinnamic acid derivative and polyphenol, with potential anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antineoplastic activities. Upon administration, caffeic acid acts as an antioxidant and prevents oxidative stress, thereby preventing DNA damage induced by free radicals. [1]
Recent Findings:
- Caffeic acid can be widely found in natural sources such as in leafy vegetables, fruits and tea extracts. In a study conducted on rats, it was shown that caffeic acid prevented the breakdown of melatonin by inhibiting the CYP1A enzyme in the liver. It has shown significant potential in herb-drug interactions. [2]
- Caffeic acid extracted from basil (Ocimum basilicum) has proved to suppress HeLa cervical cancer cells in a time-dependent manner. [3] [4]
- Propolis is a natural substance produced by bees by combining bee saliva and beeswax. It has shown potential antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. As the mechanism of action of propolis is unknown, it is hypothesized that caffeic acid is responsible for the beneficial properties of propolis. Between propolis and caffeic acid itself, results showed that both inhibited nitric oxide production of macrophages, with caffeic acid showing higher antioxidant activity. [5]
- Caffeic acid has also shown to reduce aluminium oxide-induced dementia in rats through the reduction of acetylcholinesterase activity and nitrite levels. [6]
-In rats, excessive consumption of caffeic acid may result in "squamous-cell papillomas and carcinomas...in the forestomach" and "renal tubular-cell adenomas".
Overall, caffeic acid has shown promise to be a powerful antioxidant with plentiful beneficial properties ranging from inhibiting cervical cancer to dementia. However, excessive consumption may result in tumors and adenomas.
Scientific References:
1. PubChem: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/689043
2. Effects of Caffeic Acid and Quercetin on In Vitro Permeability, Metabolism and In Vivo Pharmacokinetics of Melatonin in Rats: Potential for Herb-Drug Interaction (Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2017, Oct; 42(5):781-791)
3. Analysis of caffeic acid extraction from Ocimum gratissimum Linn. by high performance liquid chromatography and its effects on a cervical cancer cell line (Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2010, Sep; 49(3):266-71)
4. Caffeic acid induces apoptosis in human cervical cancer cells through the mitochondrial pathway (Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2010, Dec; 49(4):419-24)
5. Propolis and its constituent caffeic acid suppress LPS-stimulated pro-inflammatory response by blocking NF-κB and MAPK activation in macrophages (J Ethnopharmacol. 2013, Aug 26; 149(1):84-92.)
6. Impact of caffeic acid on aluminium chloride-induced dementia in rats (J Pharm Pharmacol. 2013, Dec; 65(12):1745-52)
Regulatory References:
1. US California Proposition 65, Chemicals known to the State to Cause Cancer
- Caffeic acid
2. WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) - Group 2B [2018]
- Caffeic acid
Safety and Hazards (UN GHS):
1. Causes skin irritation (H315)
2. Causes serious eye irritation (H319)
3. May cause respiratory irritation (H335)
4. Suspected of causing cancer (H351)
5. Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child (H361)
Potential Health Benefits For:
1. Acute Kidney Injury (PubMed ID:29968957)
2. Atherosclerosis (PubMed ID:16806235)
3. Brain Injuries (PubMed ID:18482095)
4. Chemical and Drug Induced Liver Injury (PubMed ID:18405891)
5. Edema (PubMed ID:22036979)
6. Inflammation (PubMed ID:22036979)
7. Learning Disorders (PubMed ID:18482095)
8. Melanoma (PubMed ID:20685355)
9. Memory Disorders (PubMed ID:18482095)
10. Myocardial Infarction (PubMed ID:20376586)
11. Nerve Degeneration (PubMed ID:18482095)
12. Ulcer (PubMed ID:33301711)
User Comments:
Submit