Butylene Glycol; 1,3-Butylene Glycol(in 76,399 products)
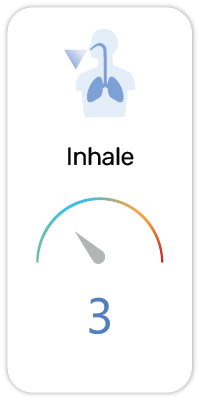
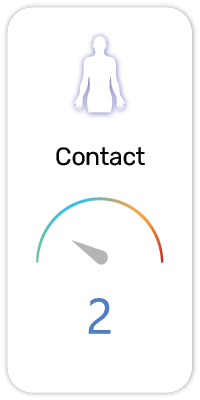
Potential Risk Index®:
About:
Functions:
1. Flavor / Flavoring / Flavor Enhancer - Provides or enhances a particular taste or smell.
2. Fragrance / Fragrance Component - Provides or enhances a particular smell or odor.
3. Humectant - Binds with water to increase skin hydration. Also enhances water absorption of the skin
4. Slip Modifier - Increases spreadability of other ingredients
5. Solvent (Cosmetics) - Enhances the properties of other ingredients
6. Viscosity Controlling Agent - Maintains or alters the thickness of a liquid, mostly used in cosmetics
1,3-Butanediol (also known as 1,3-butylene glycol, butane-1,3-diol, or 1,3-dihydroxybutane) is an organic chemical, a diol. It is commonly used as a solvent for food flavoring agents and in the manufacturing of resins.
Butylene glycol is used as solvents and viscosity decreasing agents in cosmetics and personal care products. It is used in the formulation of hair and bath products, eye and facial makeup, fragrances, personal cleanliness products, and shaving and skin care products. [1]
This is an Unapproved E-number (E1502).
Recent Findings:
Butylene glycol is used to improve the survival rates of neonatal pigs by up to 90% in a study involving ~2500 pigs. [2]
Butylene glycol has shown antibacterial and antifungal properties although its effectiveness is weaker when compared to hexylene glycol. A solution of 30% butylene glycol is as effective as a solution of 10% hexylene glycol. Both solutions killed an array of Staphylococcus and E. coli within 20 h. [3]
In long term studies where butylene glycol was fed to rats and dogs at 1.0, 3.0, and 10% levels for 2 years, no adverse effects were detected. [4]
Butylene glycol generally has limited water solubility although its fatty acid ester and nitric ester derivatives may have increased toxicity. [5]
Overall, butylene glycol has been proven to be safe in a wide range of animals from rats to pigs to dogs. Even in long term studies, no toxicity was detected. However, care must be taken when using butylene glycol as an antibacterial since its relatively weak effectiveness may contribute to antibacterial resistance.
Fun Facts:
-While it is a type of alcohol, it doesn’t typically irritate or dry out skin.
Scientific References:
1. PubChem: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/7896
2. Efficacy of 1,3-butanediol for enhancement of neonatal pig survival (Anim Reprod Sci. 2014, Aug; 148(3-4):145-52)
3. Antibacterial and antifungal properties of propylene glycol, hexylene glycol, and 1,3-butylene glycol in vitro. (Acta Derm Venereol. 1991;71(2):148-50)
4. Chronic oral toxicity of 1,3-butanediol (Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 10, 160-164; 1967 DOI:10.1016/0041-008X(67)90137-8)
5. Glycol Ethers: Ethers of Propylene, Butylene Glycols, and Other Glycol Derivatives (DOI:10.1002/0471435139.tox087.pub2)
Regulatory References:
1. E-numbers which are not found in EU FOOD
- "E1502"
2. CANADA Natural Health Products Ingredients Database [2018]
- 1,3-Butylene glycol
-
3. International Fragrance Association Transparency List [2015]
- 1,3-Butanediol
4. European Chemicals Agency
Safety and Hazards (UN GHS):
1. Causes skin irritation (H315)
2. Causes serious eye irritation (H319)
3. May cause respiratory irritation (H335)
Potential Health Concerns For:
1. Ataxia (PubMed ID:7193248)
2. Cattle Diseases (PubMed ID:4026018)
3. Chemical and Drug Induced Liver Injury (PubMed ID:2077526)
4. Dermatitis, Allergic Contact (PubMed ID:16285485)
5. Eyelid Diseases (PubMed ID:16285485)
6. Fatty Liver (PubMed ID:1787195)
7. Hypoglycemia (PubMed ID:6497141)
8. Ketosis (PubMed ID:1500562)
Potential Health Benefits For:
1. Brain Edema (PubMed ID:2219211)
2. Brain Ischemia (PubMed ID:3810756)
3. Diabetes Mellitus, Experimental (PubMed ID:7649603)
4. Dog Diseases (PubMed ID:6524722)
5. Hypoxia, Brain (PubMed ID:3810756)
6. Ischemic Attack, Transient (PubMed ID:1668814)
7. Nerve Degeneration (PubMed ID:7824183)
8. Poisoning (PubMed ID:1621360)
User Comments:
Submit