Anthocyanins(in 235 products)
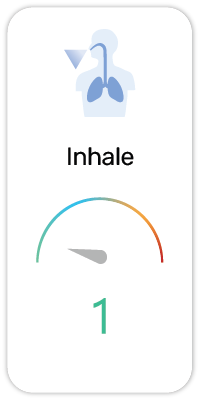
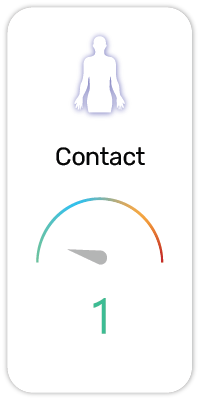
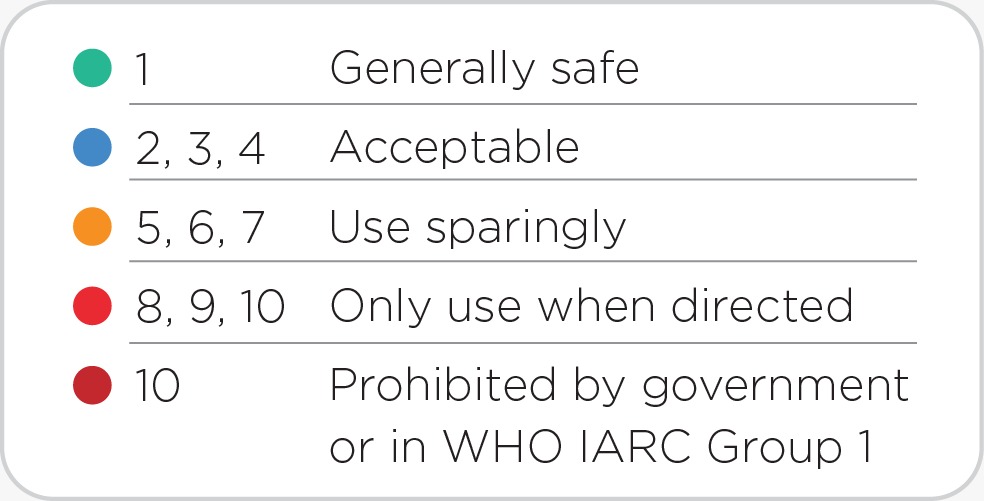
Potential Risk Index®:
About:
Functions:
1. Colorant - Pigments or dyes that are added in order to change or enhance the color.
Anthocyanins are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that, depending on their pH, may appear red, purple, or blue. Food plants rich in anthocyanins include the blueberry, raspberry, black rice, and black soybean, among many others that are red, blue, purple, or black. Some of the colors of autumn leaves are derived from anthocyanins.
Anthocyanins may also be ingested through their use as a food additive and as dietary supplements, procured as anthocyanin-rich fruit extracts, powders, and purified compounds. Anthocyanins are approved for use as food and cosmetics colorants in the EU with E number 163. It is also used a color additive and exempt from certification and permanently listed for food use in US.
Scientific References:
1. PubChem: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/145858
Regulatory References:
1. South Korea - Ministry of Food and Drug Safety - Prohibited/Restricted Chemicals
- Ref: 426
2. EU CosIng Annex IV, COLORANTS ALLOWED IN COSMETIC PRODUCTS [2017]
- Ref: IV/149
3. US FDA Color Additives Status List [2015]
- §73.169, §73.170
4. EU Approved Food Additive [2018]
- E163
5. Association of Southeast Asian Nations Annex IV - Part 1, Allowed Colorants
- Anthocyanins
Potential Health Benefits For:
1. Acute Kidney Injury (PubMed ID:24795233)
2. Chemical and Drug Induced Liver Injury (PubMed ID:30056145)
3. Diabetes Mellitus, Experimental (PubMed ID:28856781)
4. Glucose Intolerance (PubMed ID:24795233)
5. Hyperglycemia (PubMed ID:24795233)
6. Insulin Resistance (PubMed ID:24795233)
7. Liver Cirrhosis, Experimental (PubMed ID:30056145)
8. Lung Injury (PubMed ID:25451569)
9. Opisthorchiasis (PubMed ID:25447758)
10. Ventricular Dysfunction, Left (PubMed ID:28856781)
11. Weight Gain (PubMed ID:24795233)
User Comments:
Submit